Ecosystem is a basic functional unit which includes the living organisms or biotic components and non-living or abiotic components, both interacting with each other and both necessary for maintenance of life on the earth' (Odum, 1965). Ecosystem is the interaction between the biotic and abiotic components. Hence, both are interdependent to each other.
The word ecosystem was coined by A.G. Tansley (1935). He defined ecosystem as "The system resulting from the integration of all the living and non living factors of the environment". The term ecosystem was proposed by A. G. Tansley (1935).
The word ecosystem was coined by A.G. Tansley (1935). He defined ecosystem as "The system resulting from the integration of all the living and non living factors of the environment". The term ecosystem was proposed by A. G. Tansley (1935).
The term biocoenosis for ecosystem was given by Karl Mobius. The term Microcosm for ecosystem was given by S. A. Forbes. According to Fitzpatrick, 1974 a group of organisms interacting among themselves and environment is known as ecosystem.
Basic type of Ecosystem
Ecosystem is divided into two categories given below:
- Natural ecosystem
- Artificial ecosystem
(a) Terrestrial : Grassland, forest and desert ecosystem.
(b) Aquatic ecosystem : These are also divided two parts:
- Marine ecosystem : e.g. Ocean.
- Fresh water ecosystem : Running fresh water ecosystem is called lotic type e.g., rivers and standing water ecosystem is called lentic type e.g., lake, ponds, pools. Marine, which include deep bodies as an ocean or shallow ones as a sea, or estuary etc. If you want to know more detail about pond and lake ecosystem then read this - Pond or Lake Ecosystem.
By structure we mean -
- the composition of biological community including species, numbers, biomass, life history and distribution in space etc.,
- the quantity and distribution of the non-living materials, such as nutrients, water etc., and
- the range, or gradient of conditions of existence, such as temperature, light etc.
- the rate of biological energy flow i.e., the production and respiration rates of the community,
- rate of materials or nutrient cycles, and
- biological or ecological regulation including both regulation of organisms by environment (photoperiodism etc.) and regulation of environment by the organism, (nitrogen fixing organisms etc.). Thus, in any ecosystem, structure and function (rate functions) are studied together.
Components of Ecosystem
The two main components of ecosystem are:
- Abiotic
- Biotic
Abiotic components can further be divided into following three parts.
Want to know what ecology is? read this article Ecology .
- Climatic : Includes light, temperature, wind, water, etc. ultimately source of energy in the ecosystem. All plants received the solar energy and converted into chemical energy this process known as photosynthesis.
- Inorganic substances : Nitrogen, calcium, sulphur, phosphorus, etc. All of these have their cycles. The inorganic substance require for synthesis of organic substance are called nutrients. They inter into biotic components through death and decay finally returns to soil.
- Organic compounds : Protein, carbohydrates and lipids are a link between abiotic and biotic components.
Want to know what ecology is? read this article Ecology .
2. Biotic Component
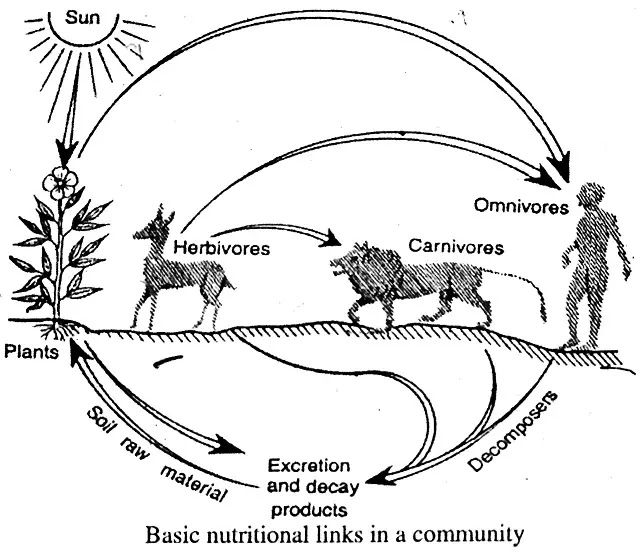
The diagram above represents the relationships of biotic components and are as follows:
(i) Producers : Producers or autotrophs (green plants) are those living members of the ecosystems which synthesize food from inorganic substances. This also includes chemosynthetic bacteria. On land, producers are usually large rooted green plants, while in deep water ecosystems they are rootless algae floating or submerged in water.
Autotrophs or producers are sometimes called primary producers as differentiated from animals which although heterotrophic manufacture, their lipid and proteins from foods taken from plants and are thus called secondary producers.
(ii) Consumers or Heterotrophs : These are heterotrophic organisms, i.e., animals which are also called macro-consumers. These ingest their food, so they are also called phagotrophs. Consumers are of the following three types:
(iii) Decomposers : (also called microconsumers) : They include bacteria and fungi which attack the dead bodies of producers and consumers and breakdown the complex compounds of dead protoplasm, absorb some of the decomposition products and release inorganic nutrients. These inorganic substances together with other organic substances are used as energy source by producers.
The biotic components include five categories of organisms, viz., Primary producers, secondary producers of first order (primary consumers), secondary producers of second order (secondary consumers), secondary producers of last order (tertiary consumers or top consumers) and decomposers, which interact among themselves and with the physical environment to form a balanced ecosystem. These five categories are recognized as energy levels or trophic levels of an ecosystem.
(i) Producers : Producers or autotrophs (green plants) are those living members of the ecosystems which synthesize food from inorganic substances. This also includes chemosynthetic bacteria. On land, producers are usually large rooted green plants, while in deep water ecosystems they are rootless algae floating or submerged in water.
Autotrophs or producers are sometimes called primary producers as differentiated from animals which although heterotrophic manufacture, their lipid and proteins from foods taken from plants and are thus called secondary producers.
(ii) Consumers or Heterotrophs : These are heterotrophic organisms, i.e., animals which are also called macro-consumers. These ingest their food, so they are also called phagotrophs. Consumers are of the following three types:
- Herbivores or Primary Consumers : These animals are the primary consumers or the ecosystem. Rabbit, Deer, Goat, Cattle, Grasshoppers, etc., are the herbivores of terrestrial ecosystem and Crustaceans, Molluses, Protozoans and many fishes are the herbivores of aquatic ecosystem.
- Secondary Consumers : These are primary carnivores, which eat herbivores. Frog, Fox, Centipedes, Fishes, Predatory birds, Lion and Tiger are the examples of secondary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers : These are secondary carnivores, which eat the secondary consumers, e.g., Snake eats insectivorous frog, Human eats fishes.
(iii) Decomposers : (also called microconsumers) : They include bacteria and fungi which attack the dead bodies of producers and consumers and breakdown the complex compounds of dead protoplasm, absorb some of the decomposition products and release inorganic nutrients. These inorganic substances together with other organic substances are used as energy source by producers.
The biotic components include five categories of organisms, viz., Primary producers, secondary producers of first order (primary consumers), secondary producers of second order (secondary consumers), secondary producers of last order (tertiary consumers or top consumers) and decomposers, which interact among themselves and with the physical environment to form a balanced ecosystem. These five categories are recognized as energy levels or trophic levels of an ecosystem.
Function of Ecosystem
The main of an ecosystem are :
1. Flow of Energy :
➠ Radiant energy of the sun enters into the ecosystem through the photosynthetic activity of plants (i.e., Producers),
➠ Travels via consumers and decomposers,
➠ Ultimately disappear in space in the form of heat energy, which new returns to the source. This phenomenon is referred to as flow of energy. The passage of materials from producers through primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary consumers is known as food chain.
3. Eco-regulation : Both organisms and the environment are regulated by each other. Thus a balance is maintained in the system.



No comments:
Post a Comment