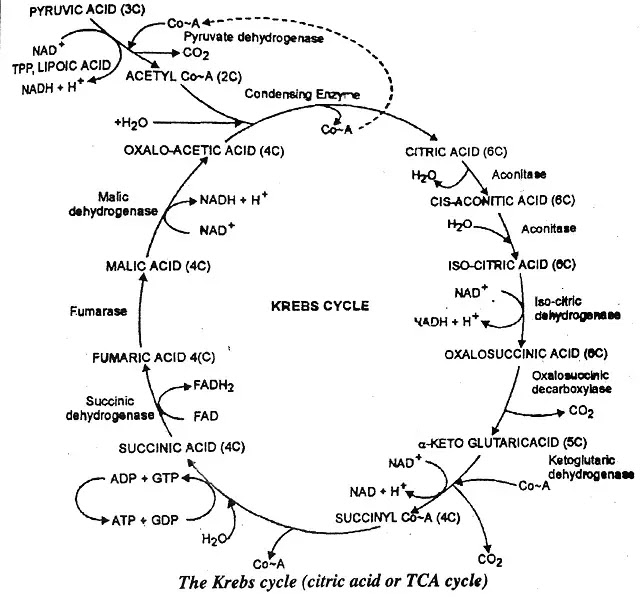
The steps of this cycle were given by Hans Krebs in 1931. Acetyl-CoA enters into Krebs cycle. Various steps of the cycle take place in mitochondria. As a result of different reactions taking place in a cyclic manner complete oxidation of Acetyl-CoA takes place. A number of krebs cycle intermediates are used in various anabolic pathways.
(1) The 2-carbon acetyl CoA is added to a 4-carbon oxalo acetic acid to form a 6 carbon citric acid in presence of a "condensing enzyme" citrate synthetase. The reaction utilizes one molecule of H2O and releases coenzyme A.
(2) By dehydration of citric acid is form cis-aconitic acid in presence of enzyme aconitase.
Aconitase
Citric acid → Cis-aconitic acid + H2O
Aconitase
Cis-aconitic acid + H2O → Isocitric acid
(4) Hydrogen atoms from Isocitric acid react with NAD to form NAD.2H forming oxalo succinic acid.
Isocitric dehydrogenase
isocitric acid + NAD → Oxalosuccinic acid + NAD.2H
Isocitric dehydrogenase
isocitric acid + NAD → Oxalosuccinic acid + NAD.2H
(5) The 6-carbon oxalosuccinic acid is decarboxylated to 5-carbon, a-ketoglutaric acid in presence of enzyme oxalosuccinic decarboxylase. One molecule of CO₂ is released in the reaction.
Oxalosuccinic acid → α-ketoglutaric acid + CO₂
Oxalosuccinic acid → α-ketoglutaric acid + CO₂
(6) The 5-carbon, α-ketoglutaric acid is oxidatively decarboxylated to form a 4 carbon succinyl coenzyme-A, in presence of enzyme α-ketoglutaric dehydrogenase. One molecule of Co-A is used up. One molecule of CO2 is released and the coenzyme NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+ in the reaction.
α-Ketoglutaric acid + NAD + CoA.SH → Succinyl-Co-A + CO₂+ NAD.2H
α-Ketoglutaric acid + NAD + CoA.SH → Succinyl-Co-A + CO₂+ NAD.2H
(7) Succinyl-Co-A is hydrolysed to form succinic acid in presence of enzyme succinic thiokinase. One molecule of H2O is used up and Co-A is released. One molecule of GDP (guanosine diphosphate) is converted to GTP (guanosine triphosphate) in the reaction. The process is termed substrate phosphorylation. The GTP can react with ADP to form ATP + GDP.
Succinyl-Co-A + GDP+ H3PO4 → Succinic acid + GTP + CoA-SH
(8) Succinic acid is oxidized to form fumaric acid in presence of enzyme succinic dehydrogenase. The coenzyme-FAD is reduced to FADH2 in the reaction.
Succinic acid + FAD → Fumaric acid + FAD.2H
Succinic acid + FAD → Fumaric acid + FAD.2H
(9) One molecule of H2O is added to fumaric acid to form malic acid. The reaction is catalysed by enzyrne-fumarase.
Fumaric acid + H₂O → Malic acid
Fumaric acid + H₂O → Malic acid
(10) Malic acid is oxidized to form oxaloacetic acid in presence of enzyme malic dehydrogenose one molecule of NAD is reduced to NADH + H in the reaction.
Malic acid + NAD → Oxaloacetic acid + NAD.2H
Malic acid + NAD → Oxaloacetic acid + NAD.2H
%20%20Definition,%20pathway.webp)


No comments:
Post a Comment