Reproduction in Yeast
There are two main methods of reproduction in yeast -
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction
Vegetative Reproduction
There are two main methods of vegetative reproduction in yeast -
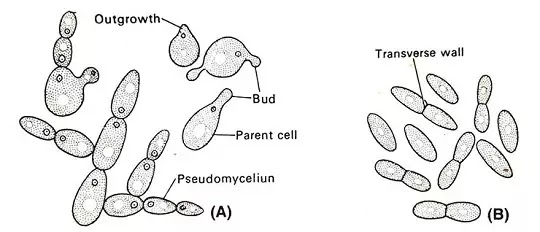
- By Budding – In yeast, the bud is formed in a favorable condition. There is a slight outgrowth in the yeast wall. This outgrowth gradually increases to form a bud. This bud separates from the mother cell and produces new yeast.
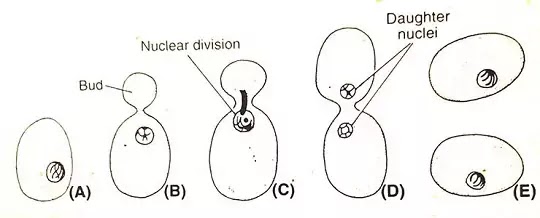
reproduction by budding in yeast
- By Fission - Fission in yeast is caused by the formation of a transverse wall. There is a collapse in the middle wall of the yeast and it grows to form the transverse wall. It separates from the wall and forms Daughter Yeast.
Sexual reproduction in yeast takes place under unfavorable conditions when there is a lack of food. This is done by conjugation. Fusion occurs between two identical cells. The zygote formed after fusion acts as an ascus and forms ascospores. Yeast does not have specific types of sex organs for sexual reproduction.
There are three main methods of sexual reproduction in yeast -
- Haplobiontic Type
- Diplobiontic Type
- Haplo-Diplobiontic Type
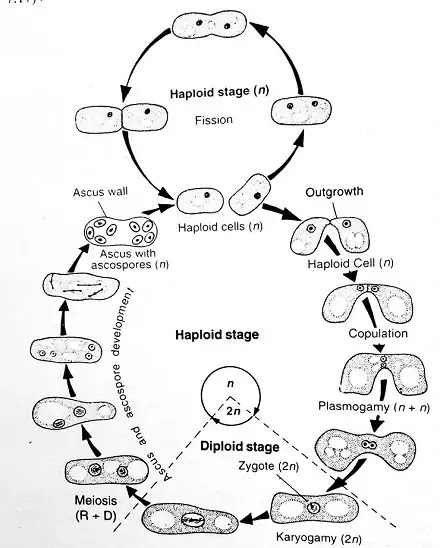
Haplobiontic Type
- In the Haplobiontic Cycle of Yeast, Haploid (Haploid = n) stage is more and Diploid (Diploid = 2n) stage is less. In this cycle, the diploid state is for a short period of time.
- Haplobiontic type reproduction is found in Schizosaccharomyces octosporus yeast.
- It consists of two diploid yeasts which are structurally and functionally similar. In these, a beak-like structure is formed, which is called Outgrowth. Together they form a tube called Conjugation Tube.
- The wall between the Conjugation Tube melts away. In this tube itself, the nuclei of both the cells join together to form a zygote. This is the diploid state.
- In this Diploid Stage, first Meiosis and then Mitosis Division takes place, due to which 8 Ascospore are formed. This Ascus is Haploid.
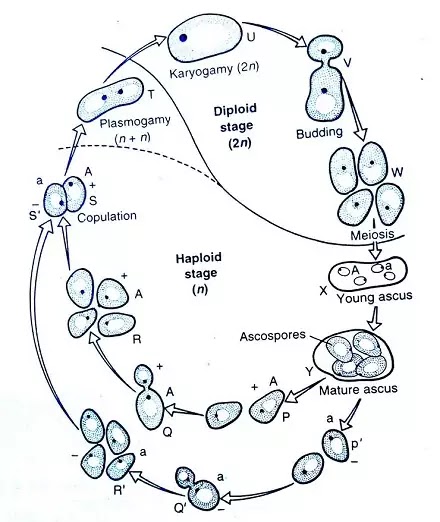
Diplobiontic Type
- The diplobiontic cycle is found in Saccharomycodes ludwigii. In this, the Diploid state is for a longer period and the Haploid state is for a shorter period of time.
- This cycle starts from the diploid stage and ends at the diploid stage and there is also some haploid stage in this cycle.
- Meiosis gives rise to four haploid ascospores by division. These ascospores are not independent from the ascus and in the ascus itself, two opposite types of ascospores combine with each other, this is called plasmogamy.
- Karyogamy is formed by the fusion of both the nuclei. Germination takes place due to the meeting of this Karyogamy and Sprout Mycelium is formed. It is Diploid.
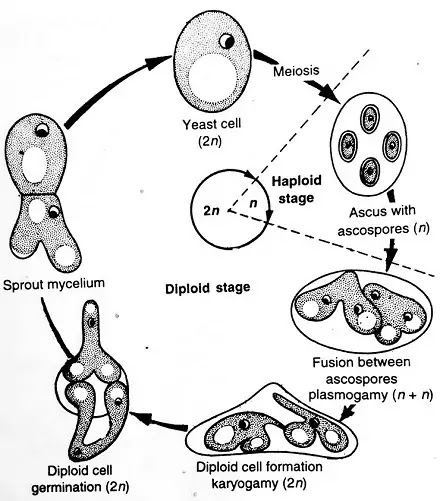
- Haplo-Diplobiontic Cycle is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- In this cycle, both Haploid and Diploid stages are equal. Half stage is Haploid and half stage is Diploid.
- Mitosis division occurs twice in the diploid stage, leading to the formation of four diploid nuclei.
- In this diploid nucleus young ascus is formed by meiosis division. These ascus are haploid.
- In this Haploid Ascus, meiosis takes place and Diploid nucleus is formed by Plasmogamy and Karyogamy.



No comments:
Post a Comment