Mediterranean diet : definition, components, key features, Health benefits
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that has gained immense popularity in recent years as a healthy and sustainable approach to food. It is based on the traditional foods and cooking styles of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy and Spain. In this article, we'll explore the Mediterranean diet, including what it is, what to eat, and the benefits of following it.
What is the Mediterranean Diet?
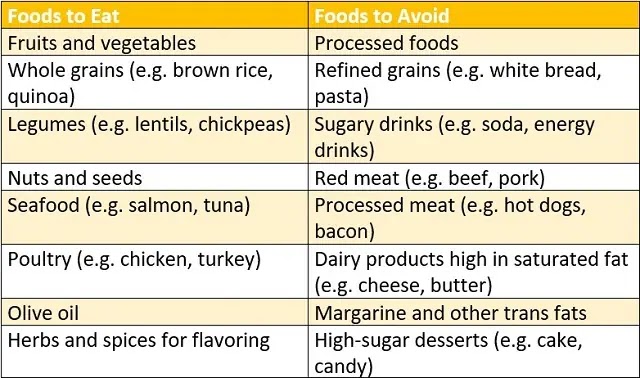
The Mediterranean diet is a plant-based, whole foods diet that emphasizes eating fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, fish and healthy fats like olive oil. It's also low in processed foods, red meat and added sugars, and moderate in dairy and poultry. There are many benefits we get from following a Mediterranean diet, including a lower risk of heart disease, diabetes and other chronic conditions, as well as better weight management and cognitive function.
What should we eat and what should we not eat in the Mediterranean diet?
we should eat
The typical Mediterranean diet consists of fresh, whole foods that are locally sourced and in season. Examples of Mediterranean dishes and recipes include:
- Greek salad with fresh vegetables, feta cheese, and olive oil dressing
- Italian minestrone soup with whole-grain bread
- Spanish paella with seafood, rice, and vegetables
- Hummus with raw vegetables for dipping
- Grilled fish with lemon and herbs
- Fresh fruit for dessert
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the importance of fresh, whole foods in the diet and recommends avoiding processed foods and added sugars.
We should not eat
Foods to avoid on the Mediterranean diet include:
- Sugary drinks and snacks
- Processed meats such as bacon and sausage
- Fast food and junk food
- Refined carbohydrates such as white bread and pasta
These foods can have negative effects on health and should be limited or avoided altogether in a Mediterranean diet.
Typical Mediterranean breakfast
A typical Mediterranean breakfast is a light and refreshing meal that usually includes whole-grain bread, fresh fruit, yogurt, and nuts. It is a simple and healthy way to start the day, providing a good balance of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. Some popular Mediterranean breakfast options include:
- Greek yogurt with fresh berries and honey
- Whole-grain toast with avocado, tomato, and a drizzle of olive oil
- Omelette with spinach, feta cheese, and olives
- Freshly squeezed orange juice
- Herbal tea or coffee
Ideas for Mediterranean breakfast recipes can be found in many cookbooks and online resources. It is easy to modify these recipes to include local ingredients and flavors.
Mediterranean diet with Indian food
By concentrating on the essential elements of the diet, such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and nuts, the Mediterranean diet may be adapted to Indian cuisine. Some examples of Indian foods that fit into the Mediterranean diet include:
- soup made of lentils, veggies, and herbs.
- curried chickpeas and brown rice
- grilled fish with veggies and Indian seasonings
- Tandoori chicken served with roasted veggies on the side
- salad of mixed vegetables dressed in olive oil and lemon
Saturated fats and processed foods, which are frequently present in Indian food, should be used in moderation.
Components of Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is made up of eight key components that form the foundation of a healthy eating pattern. These elements include:
- Vegetables and fruits
- whole grains
- Nuts and legumes
- Seafood and fish
- Olive oil and several additional healthy fats
- spices and herbs
- a red wine (in moderation)
- poultry and dairy (in moderation)
The Mediterranean diet places a strong emphasis on adding each of these elements into the diet in a balanced way since each one of them contributes to improving health and wellness.
Key features and Health benefits of the Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is an eating pattern that emphasises the consumption of fresh, whole foods that are nutrient- and flavor-rich. Three essential aspects of the Mediterranean diet are as follows:
- Emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods: Consuming entire, unprocessed foods such fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds is encouraged by the Mediterranean diet. Because of the minerals, fibre, and antioxidants that these foods contain, they can help maintain good health and stave against chronic illnesses.
- Use of healthy fats: Olive oil, nuts, and seeds, as well as other plant-based fats, are prioritised in the Mediterranean diet. Omega-3 fatty acids, which have been demonstrated to enhance heart health, lower cholesterol levels, and lessen inflammation in the body, are present in these fats in significant amounts.
- Moderate intake of dairy, fish, and meat: Dairy, fish, and meat are all part of the Mediterranean diet, but they should only be eaten in moderation. The diet, on the other hand, emphasises plant-based foods as the primary source of nutrition. Ingesting less saturated and trans fats, which raise the risk of heart disease, can assist.
health benefits
The Mediterranean diet is crucial for fostering health and wellbeing. Many health advantages of this diet have been connected to it, including:
- Improved heart health: The Mediterranean diet focuses on natural, unprocessed foods and heart-healthy fats to help lower cholesterol levels, inflammation and other heart-related problems.
- Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes: The emphasis on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in the Mediterranean diet can help control blood sugar levels and lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Improved brain function: Omega-3 fatty acids are high in fish, nuts and seeds found in the Mediterranean diet. It helps in better cognitive function and reducing the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- Weight management: The Mediterranean diet's emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and healthy fats can help people keep their weight under control.
Overall, the Mediterranean diet can be considered a balanced and sustainable way of eating that promotes health and well-being.
The Mediterranean diet is a manner of eating that is widespread in the areas around the Mediterranean Sea, hence it is not exclusive to any one nation. The Mediterranean diet, however, is particularly well-known in several nations and civilizations. These include Greece, Italy, Spain
In conclusion, we can say that Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that emphasizes fresh, whole foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, legumes and seafood and limits processed and sugary foods. . It is not confined to one country, but is common in various regions around the Mediterranean Sea.
The Mediterranean diet is not just a way of eating, but also a way of life, which reflects the cultural values and traditions of the people living in the region. If you're interested in following the Mediterranean diet, it's important to focus on incorporating key components of the diet into your daily routine, as well as enjoying the social interactions and physical activities that are integral to the Mediterranean lifestyle.



No comments:
Post a Comment